Just like human beings have a life cycle, so do products. These life cycle phase is divided into four stages and is a concept used by management and by marketing professionals as a factor in deciding when it is appropriate to increase advertising, price reduction, new market expansion as well as redesign packaging. It is an important four-stage structure in the life of any product.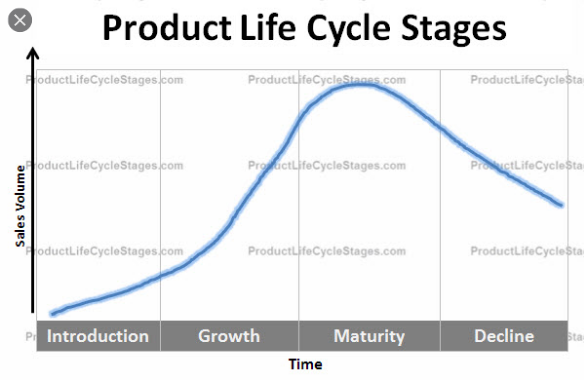
What is Product Life Cycle?
A product life cycle is the growth of a product through the four stages of its time in the market that is broken into four stages: the introduction stage, the growth stage, the maturity stage, and the decline stage.
How Product Life Cycle Works – Product Life Cycle Development
The stage of a product’s life cycle affects the way it is marketed to consumers. While a new product needs to be explained, a mature product, on the other hand, needs to be differentiated from its competitors.
An idea is what births a product. The product then undergoes research and development and when it is found to be feasible and potentially profitable, the product is then produced market and introduced into the market.
Product Life Cycle Definition – Investopedia
https://www.investopedia.com › … › Small Business
The life cycle of a product is broken into four stages—introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. This concept is used by management and by marketing …
What is a Product Life Cycle? (Definition, Stages and Examples)
https://www.twi-global.com › technical-knowledge › faqs
A product’s life cycle is usually broken down into four stages; introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Product life cycles are used by management and
Exploit the Product Life Cycle – Harvard Business Review
https://hbr.org › 1965/11 › exploit-the-product-life-cycle
The usual characteristic of a successful new product is a gradual rise in its sales curve during the market development stage. At some point in this rise
The 6 Stages of the Product Life Cycle – HubSpot Blog
https://blog.hubspot.com › marketing › product-life-cycle
The maturity stage is when the sales begin to level off from the rapid growthperiod. At this point, companies begin to reduce their prices so
The second phase is the product introduction phase, which basically involves a substantial investment in marketing campaigns geared at raising customers aware of the product and its benefits. If the product launch is successful, then it will enter the growth phase. As the demand grows production is increased, and the availability of the product expands. Here is what happens in the introduction phase:
- Establishment of branding and affirmation to the market of the quality of the new product.
- An initial low pricing policy startup to gain access to the market. With little competition, the price may be high initially, so that the organization can recoup development costs.
- Deciding on a distribution model to get the product onto the market and widely spread.
- Promoting the product via aiming it at targeted groups like online forums.
Over time, the product matures and enters its most profitable stage, and costs of production and marketing decline. Howbeit, it inevitably begins to take on increased competition as other companies emulate it’s a success, sometimes with enhancements or lower prices. At this stage, the product may lose market share and begin its decline. The growth phase involves the following:
- Adding features that will differentiate the product from the competitors that enter the market or are already in the market.
- Reducing price to match competitors.
- Revising distribution channels and dishing out incentives to encourage stores to stock the original product in preference to newcomers.
- New promotions are targeted at showing differences between products.
At the decline stage, the business will likely consider the following:
- Keeping the product on the market but with added features or removing features or better still finding new uses for it.
- Reducing costs and production, on the other hand, maintaining it just as a niche segment of the market.
- Discontinuing the product or relinquishing the production rights to another company.
Disadvantages of Life Cycle Management
Most new products fail at the first phase of their life cycle, which is the introductory stage, this makes the failure depleting in terms of resources for most companies because an investment of substantial money and time has been put into research, development, and production.
Because of this, most companies prefer to clone other people’s success rather than start one.


